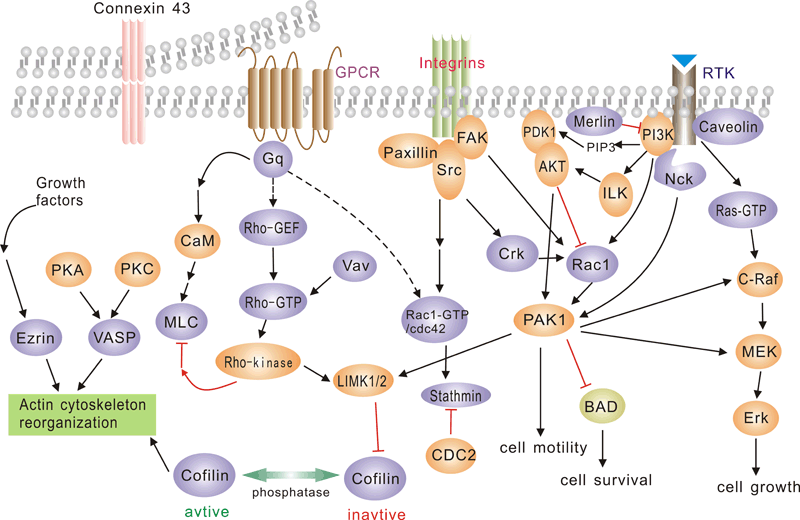
Pathway description:
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. GPCRs are activated by an external signal in the form of a ligand or other signal mediator. This creates a conformational change in the receptor, causing activation of a G protein.The extracellular parts of the receptor can be glycosylated. These extracellular loops also contain two highly-conserved cysteine residues that form disulfide bonds to stabilize the receptor structure.
The family of p21-activated protein kinases (PAKs) is composed of serine-threonine kinases whose activity is regulated by the small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases), Rac and Cdc42 In mammalian cells, PAKs have been implicated in the regulation of mitogen-activated protein cascades, cellular morphological and cytoskeletal changes, neurite outgrowth, and cell apoptosis.
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinase involved in integrin-mediated control of cell behavior. Following cell adhesion to components of the extracellular matrix, FAK becomes phosphorylated at multiple sites, including tyrosines 397, 576, and 577. Tyr-397 is an autophosphorylation site that promotes interaction with c-Src or Fyn. Tyr-576 and Tyr-577 lie in the putative activation loop of the kinase domain, and FAK catalytic activity may be elevated through phosphorylation of these residues by associated Src family kinase. The clustering of integrins at these sites attracts a large complex of proteins and initiates intracellular regulatory processes, by which such events as cell migration and anchorage-dependent differentiation are controlled. FAK is a protein tyrosine kinase which is recruited at an early stage to focal adhesions and which mediates many of the downstream responses. FAK subsequently interacts with a number of down-stream signalling proteins, including the adaptor protein Grb2 and the p85 _-subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3 kinase)
References:
Daniels, R. H. & Bokoch, G. M. (1999) p21-Activated protein kinase: a crucial component of morphological signaling? Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 350-355.
Lei, M. et al. (2000) Structure of PAK1 in an Autoinhibited Conformation Reveals a Multistage Activation Switch . Cell 102, 387-397
Joost P, Methner A(2002) Phylogenetic analysis of 277 human G-protein-coupled receptors as a tool for the prediction of orphan receptor ligands. Genome Biol 3 (11), research0063.1-0063.16.
Bjarnadottir TK. et al. (2006) Comprehensive repertoire and phylogenetic analysis of the G protein-coupled receptors in human and mouse. Genomics 88 (3), 263-73.
Astier A. et al. (1997) The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase is tyrosine-phosphorylated after beta1-integrin stimulation in B cells and binds to p130cas. J Biol Chem.272,228–232.
Avraham S,.et al. (1995) Identification and characterization of a novel related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK) from megakaryocytes and brain. J Biol Chem. 270,27742–27751.


